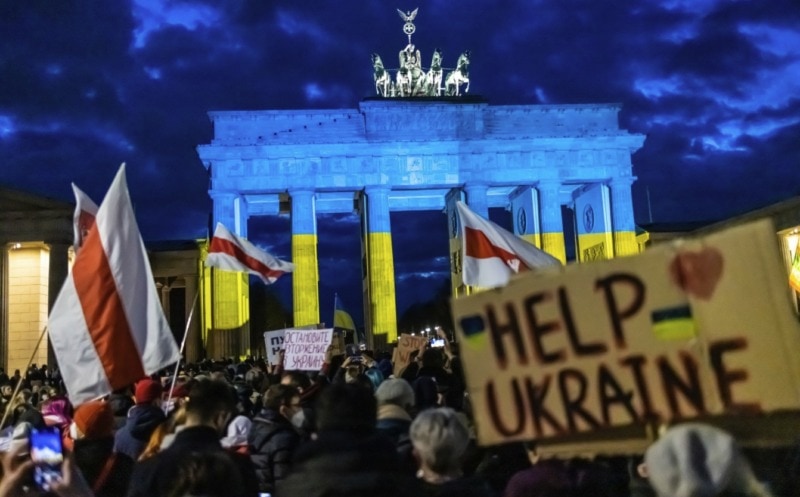
Last October, I sat in the office of Klaus Emmerich, the chief union representative at the Garzweiler brown-coal mine in western Germany, as he shared his misgivings about the country’s celebrated plan to stop burning coal. Germany’s build-up of renewable energy was lagging and, given that coal accounts for more than a quarter of its total electricity supply, that meant it would have to rely on another energy source for the time being: natural gas, which came mostly from Russia. “We’re giving ourselves over to the Russians,” Emmerich told me. “I have a bad feeling about it.”

Credit: Hannibal Hanschke/Getty
Five months later, Emmerich’s premonitions have borne out, powerfully. President Vladimir Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has unleashed civilian and military carnage, ravaged cities and sent some two million people fleeing the country. As its effects have rippled across Europe and the world, one consequence has gone underexamined: The invasion has upended the political and economic policies of Germany, where the government has reconsidered its long-planned energy transition; undone a […]











It seems like Germany is in a difficult situation. I hope Russia will help and not hurt Germany. I like Germany after having spent 3 years there during the 60’s and finding them a very loving people and easy to get along with.